When it comes to ranking on Google, enterprise websites are in no way comparable to small business websites.
Enterprise websites are large and complex websites that belong to big organizations and contain hundreds of thousands of web pages. Hence, there are more pages to work on and more resources to use, which require bigger budgets.
Although 88% of enterprise-level marketers use content marketing to create demand, generate leads, and boost product sales, only 28% of them drive results for companies, according to the Content Marketing Institute Report.
That’s why you need to be strategic and work with a digital marketing company that understands the technical, on-page, and off-page aspects of enterprise SEO.
Enterprise websites have unique goals when it comes to SEO. For instance, large organizations already have brand recognition and would not need to compete with smaller companies to advertise or build brand recognition with their website.
Instead, one of the major SEO objectives of any large company is to maintain its online prominence, organic rankings, and brand reputation, as well as to stay successful in edging out both current and future competitors.
Hence, apart from having hundreds if not thousands of web pages, enterprise websites don’t share similar SEO objectives with smaller websites. That is why enterprise SEO calls for careful consideration and differs greatly from basic SEO.
According to a study, about 51% of all website traffic comes from organic search – SEO.
This calls for a huge competition among brands and this affects all enterprise websites too.
Therefore, to outperform the competition, enterprise companies must put in all efforts to improve upon their visibility – website, web content, and blog posts – and perform well in organic search.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll explain what large businesses and enterprise companies need to know about enterprise SEO and some practical steps they can take to rank their websites higher in Google Search Engine Research Pages (SERPs).
Let’s dive in.
Step #1: Website Structure
Enterprise SEO cannot just start with keywords research, on-page optimization, and Google rankings, else business executives would be missing an enormous opportunity.
Yes, enterprise companies need to think about SEO holistically i.e., from website crawling to conversions if they want to achieve any meaningful results from their SEO efforts.
Therefore, companies need to first dive deeper and focus on fixing their website structure and technical issues to improve searchability, visibility, and User Experience (UX). Here’s an example of an eCommerce enterprise site architecture.
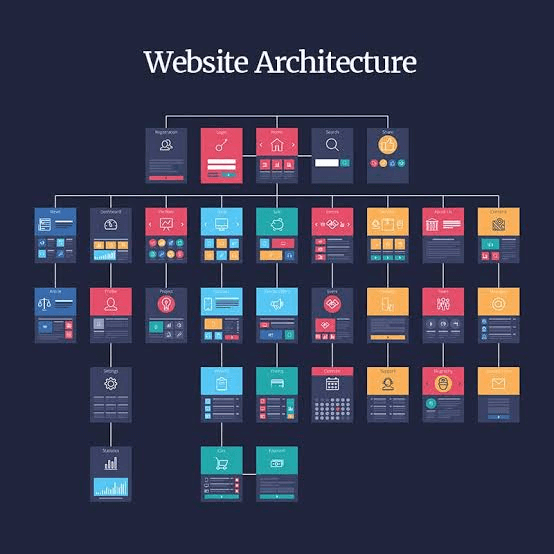
Fixing the entire website structure starts with fixing the website’s technical foundation, how Google crawls and indexes it, and how its target audience engages with it.
Did you know that Google only crawled and indexed half the pages on enterprise websites in 2018? And this means that enterprise companies cannot rank or generate as much organic traffic and revenue as possible for their business.
The problem is neither with a large number of web pages on enterprise websites nor with Google crawler that is always at its best to crawl all web pages.
But with poor website structure and technical issues, which are responsible for bad website indexation and crawling issues.
If you’re a business manager, CEO, or top-level executive, bear in mind that no matter how you prepare your web content to target keywords or rank high on Google SERP, if Google can’t easily crawl your pages and users struggle to navigate from one web page to the other, the keyword and Google rankings efforts will not likely generate the desired results.
To mitigate this issue and rank high on Google results pages (especially the first page), companies with big websites must first carry out a thorough technical website audit.
Ensure that your website has a solid structure. Carefully check for and fix any broken links, fix all keyword cannibalism issues, and resolve any duplicate content issues.
You can use the Screaming Frog tool to find duplicate pages on your website.
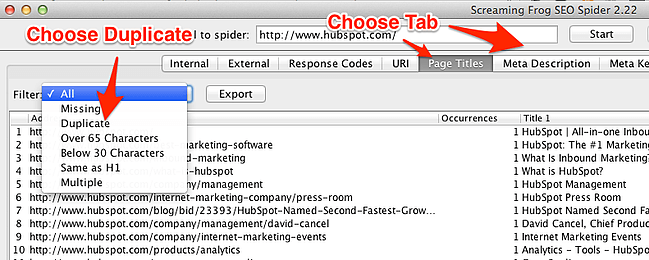
Check that all necessary web pages are well-indexed to allow Google crawlers. If you notice any bad internal linking, make necessary tweaks to align your website with your SEO strategy.
And also check for indexation and crawlability and mobile-responsiveness.
You may need to conduct a regular and thorough technical audit to ensure that all priority technical issues have been addressed and are timely addressed in the future.
Step #2: Keywords Research and Competitive Analysis
If you have thoroughly attended to and fixed all of your website structure and technical issues, you can move on to keyword research and analysis. Here, I’m using SEMrush to do a quick analysis on Reddit.
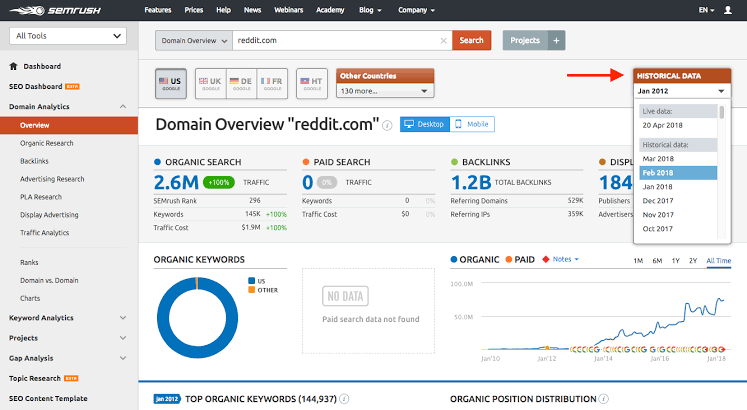
To date, keywords reveal the intent of your target audience. It shows what they’re searched for on Google to find your website through organic search.
Therefore, it is very important to target the right queries or keywords that your audience is searching for.
Sometimes, though, some huge brands use keywords they believe are closely-tied to their products and services. This is wrong as they must tailor their keywords to the language of the audience.
For instance, enterprise companies may use some technical jargon (that makes sense to them) that aren’t understood by their target audience.
To make maximum impact, the keyword research must be adjusted to suit the language the audience understands.
Business managers must carry out a thorough SERP analysis by examining conversations, current clients, leads, emails with prospects, and feedback, to understand their language and need.
They must also look at search queries and topics that are currently ranked high in Google SERPs from search results for their target keywords using the following features:
- Related searches
- People also ask
- Google autocomplete suggestions
- Other advanced search features.
More so, to ensure that the target keywords are aligned with the needs of the audience, it is important to understand the search intent of the audience.
You may want to brainstorm on the search intent, needs, interests, and potential searches of your target audience. You should also analyze your competition to see which keywords they’re targeting.
No, you don’t need to do this manually. You can use third-party search analysis tools such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Alexa to fully audit your competition.
To achieve the best result, try a good combination of both head keywords, which are highly competitive and less-competitive long-tail keywords.
Short keywords (or head keywords) can generate a lot of traffic while long-tail keywords generate fewer visitors per month but they can be very targeted. An example of a short keyword is “medical apps” while an example of a long-tail keyword is “medical apps for doctors.”
Being a large website, keyword research and competitive analysis may not be an easy feat for an enterprise website. But the following steps can simplify the whole keyword research process:
I) Automation:
Every SEO strategy is built around using relevant keywords that a company wants to rank for. Enterprise websites such as Adobe, Microsoft, Disneyland, and the likes are huge with thousands of pages, manual keyword research is not an option.
Your company’s website may not be as huge as the ones above, but if it’s large enough with hundreds of pages (especially eCommerce websites), then you need to automate the keyword research process.
There are several enterprise SEO tools that business managers can use to automate the whole process of keyword research. These keyword research tools are well-designed to fit in different enterprise SEO platforms.
We like to use SEMrush and KeywordTool.io. They work pretty well but you need to master the features to get the most out of them.
II) Analyses:
Researching and generating keywords is not enough. Competitive analysis is also needed to select the most efficient and relevant keywords to build your enterprise SEO strategy.
Keyword competitive analysis includes:
- Analyzing keywords’ competition: This involves analyzing keywords to determine whether they’re low, medium, or high-performance search terms based on the number of competing websites.
- Analyzing keyword difficulty score: This involves determining the strength of a given keyword and the number of competitors it has.
Keyword competitive analysis is crucial as it helps to evaluate the likelihood of getting good positions for the target keywords.
Else, enterprise websites will only expend all of their time and efforts since the SEO team will strive to rank for the wrong keywords.
III) Keyword Mapping:
As much as possible, you want to avoid keyword cannibalism (ranking two or more of your web pages for the same keywords or search terms). So, it’s important to ensure that your target keywords are mapped to the right pages.
You don’t even need an expensive spreadsheet to map out keywords. Here’s a good example of keyword mapping using Google sheets:
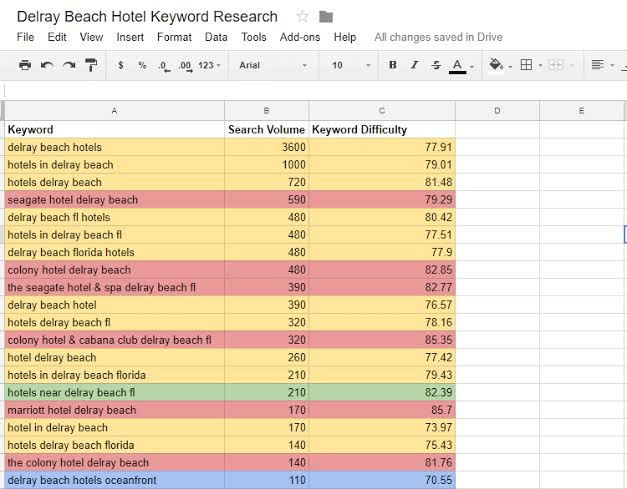
For enterprise websites with hundreds of web pages, it’s advisable to divide all keywords into groups. This will help to properly map keywords and help businesses to account for all the keywords and web pages they’re optimizing.
This has been a common problem for most enterprise websites.
For instance, imagine a situation where an audience searched for a pure informational search query but unexpectedly the product page also pops up in the first SERP (this may lead to a poor UX and is not good for Google ranking as well).
IV) Find Striking Distance Keywords:
Ever heard of this ‘term’ before? Anyways, striking distance keywords are targeted keywords that rank a company’s web page on Google’s results pages without building many backlinks or any backlinks at all.
They can be branded keywords or product names that you can target and rank very quickly.
For example, HubSpot CRM app, HubSpot Academy, HubSpot SEO tool, are easy pickings for the company.
Of course, HubSpot ranks at number #1 for these search terms already, but if they weren’t, a piece of content that’s published on the company’s domain will outrank a generic website that’s already ranking for it.
If you notice that some of your ‘striking distance’ keywords are ranking in positions 11 and 20 or on Google’s second page, do some tweaking to optimize them and get your web page pushed to the top 10 results.
The benefits of striking distance keywords are incontestable. They move enterprise websites to the first SERP faster and with less effort.
Step #3: Creating Highly-Focused Content
Once you have carefully followed the step above to get relevant and target keywords to rank for on Google, the next step involves creating highly-focused content to address the keywords and appeal to the searcher’s intent.
Content is very crucial for enterprise websites to earn quality inbound links and organic traffic, which, in turn, will boost their ranking and stronger brand presence.

As an enterprise website, it is very important to create consistent, highly-focused, and authoritative content the provides helpful information to your audience.
Depending on your products and services, as well as your vision, your content idea may vary (and it should).
For instance, your content could educate your audience about the latest industry advancements and how that affects their businesses or you could create content that answers a question your customers are asking.
More importantly, create content that addresses the pain points of your audience as well as solves their problems and challenges.
Content like this will not only engage with your target audience but will also position your company as one of the industry leaders.
Companies need to be very careful as content has some pitfalls if not well-managed, especially large-scale content projects.
Due to the size of the website, all the steps involved in the optimization process are always time-consuming.
Moreover, a lot of people have access to content production and posting on enterprise websites, which may lead to content inconsistency and duplication.
To create consistent, highly-focused, and authoritative content, enterprise companies should consider the following tips:
I) Dynamic optimization:
As stated above, updating and optimizing high-quality content involves a lot of work and time. Sometimes, there may not be sufficient time to update all the existing pages that may contain some outdated information.
But nobody wants to feed on stale information. That is why enterprise companies must think of a way to optimize and update their websites quickly and without stress.
One surefire way to achieve this is by dynamic optimization.
Dynamic optimization deals with the automation of the content optimization process. This strategy drastically decreases the amount of manual work and time needed to optimize and update web pages irrespective of their numbers.
What business managers have to do is create a standard template for the most significant parts of their pages, which include:
- Content structure
- Page titles
- Meta description and tags
- Images,
- image titles and description
- Proper markups, etc.
Dynamic optimization is already built into some content management systems (CMS).
II) Remove Duplicate and Thin Content
The bigger a website is, the higher the chances that it will have duplicate content. While Google doesn’t penalize your website for this, duplicate content confuses crawlers on which web content to consider as primary and index.
Duplicate content as impedes good user experience.
As a result, Google (being a machine) may rank a different, less important web page on your website (but with the same content) higher than your primary web page on SERP.
Therefore, you need to get rid of duplicate web content on your website.
But if for any reason you would need to create duplicate web content, let robots.txt file know which of the web content is primary and which is duplicate.
This can be easily achieved by applying the “301 redirects” or the “rel=canonical attribute” to all the duplicate pages. You can also mark all the duplicate pages with nofollow, or noindex, tags.

More so, remove pages with content that brings no value to your audience or pages with thin content.
Did you know that thin content or content of no value to the audience affects the quality of your website? That’s more reason why you must get rid of thin content.
There are several ways to go about removing thin content: you may rework and expand the content to make it more valuable.
You may delete the page if possible or if the page has no value, just remove it. However, if you don’t want to delete a page, you may hide it from being indexed by Google using the nofollow, or noindex, tags.
Step #4: Strategic Link Building
Now that you have created and published high-quality content with target keywords strategically placed. The next step involves strategic link building to earn links through outreach and guest blogging.
Strategic link building is simply the process of employing proven strategies and tricks to encourage other websites to link back to your website.
Links are crucial to Google ranking. Hence, strategic link building should be part of the growth hack and holistic SEO strategies of every large company.
More so, all enterprise companies should be interested in building links to promote their useful content (such as articles, videos, podcasts, white papers), generate referral traffic, and increase their website’s authority.
Note that not all content is good for link building, but only niche-specific content brings good quality backlinks.
Every enterprise company that cares about the long-term success of its website should invest in guest blogging and outreach campaigns — these two strategies are some of the best for gaining natural links that Google will reward.
The process of buying links or achieving them through manipulative ways (i.e., black-hat SEO) may eventually get your website banned from Google SERPs.
Although natural link building takes lots of time and is a difficult process, they remain the best and have a greater impact on your rankings on the organic search, especially if the links come from high-authoritative websites.
Strategic link building is also important to business managers because it is one of the major Google ranking factors.
According to Google:
“In general, webmasters can improve the rank of their sites by increasing the number of high-quality sites that link to their pages.“
Given the importance of inbound links, let’s briefly discuss some of the approaches we take to build high-quality and natural links for our clients’ websites.
- Content Creation and Promotion
Enterprise websites must create compelling, niche-specific, unique, and high-quality content that people will naturally want to tell others about, reference, and link to.
Nobody likes irrelevant content, let alone telling others about it. Hence, you must always create engaging content that your ideal customers would like.
Don’t forget that you also have to use relevant and popular keywords to enhance the searchability and visibility of your content before you can expect anyone to find it and link to it.
You can also submit engaging and great content with backlinks as guest blogs or posts on social media platforms. All of these efforts will help you to get trusted links from sites with good link profiles.
- Reviews and Mentions
You can build relationships with influencers, popular bloggers, or people with large social media following in your niche to put your brand, website, product, or service in front of their large devoted followers or subscribers.
This can earn you a decent number of links, as long as the content is interesting, well-formatted, and helpful.
Using brand monitoring tools such as MentionLytics, you can track every mention of your website, product, or brand across the web.
And whenever you find a linkless mention, you can ask the webmaster or blogger to consider linking back to your website.
- Links from Partners
An enterprise company can ask their partners or other companies that work with them or use their products or services to link to their website.
Remember that relevance matters so building links from other websites in the same niche or industry as your company will have more value than building links from some random and unrelated websites.
- Leverage Your Partnerships
Most large companies are a parent or sister company to several other established businesses.
You should begin your link building campaigns from these partnering websites. This is an opportunity to share relevant promotional and mutual content that links to related products or services.
Strategic link building takes a while, especially with highly-authoritative websites, but every effort you put in is well worth it.
Don’t forget that buying backlinks is against Google’s webmaster guidelines. Google frowns at it, so you should stay away from it.
Step #5: Improve Site Speed
If you had religiously followed the four steps above, your website should be ranking high on Google SERP and generating organic traffic.
But did you know that over 45% of your clients expect your web page to load in 3 seconds or less and would likely leave your web page if it doesn’t load in a few seconds?
And for visitors that decide to endure the long loading time (possibly because of the usefulness of your content), the slow load times may discourage them from returning in the future as over 75% of clients said they would not return to a slow-loading website.
That is why you must also focus on improving and optimizing your site’s speed and not just the content – if your website is too slow, it will cost you clients and sales.
Aside from the fact that page speed is one of Google’s ranking factors, a one-second delay in page load time can result in a huge loss for your business.
A recent report revealed an average bounce rate of 9% for web pages that take 2 seconds to load and an average bounce rate of 38% for web pages that take 5 seconds to load.
If Google made site speed its priority, you should make yours too.
According to Google, here’s a list of recommended practices that can improve your overall site speed and increase your Optimization Score in Google PageSpeed Insights:
- Enable data compression: This cuts down the time spent to load your page. It also improves your page rendering time — which means better data usage for visitors.
- Implement a caching policy: The absence of a caching policy would lead to several round trips between the client and server during the resources fetching process. This would lead to delays, page rendering blocking, and longer loading time for your page.
- Improve server response time: More than 50% of mobile users will leave your website if it doesn’t load within 3 seconds.
- Optimize CSS delivery: If your website is built with CSS, then it would need to process CSS before page rendering. But if the CSS is full of render-blocking external stylesheets, there would be a delay in rendering resulting in longer loading time.
- Optimize image data: Since images account for over 55% of an enterprise website size, using heavy images would significantly slow down the rendering of the pages.
- Prioritize visible content: Your above-the-fold content should not exceed 14.6kb compressed for faster page loading.
- Reduce CSS, HTML, and JavaScript resources: This will subsequently reduce the amount of redundant data from the resources delivered to visitors.
- Remove render-blocking JavaScript: Aside from removing render-blocking external stylesheets, render-blocking JavaScript should be removed too. Every time a web browser encounters your page’s HTML, it has to stop to execute this script, which slows down the rendering process. Imagine what happens if there are lots of HTML tags that need to be rendered.
- Minimize landing page redirects: Try as much as possible to avoid landing page redirects. They slow down your page rendering, which affects user experience negatively.
If you follow the nine practices above carefully, you’ll notice a significant improvement in your page speed. Note that improving the overall site speed takes time, so be patient.
These are very important enterprise SEO steps that every business manager must follow to rank their website high in Google.
Enterprise SEO Results and Case Studies
Which large companies have seen results after implementing an enterprise SEO campaign?
Well, let’s look at some case studies.
T-Mobile
Presently, T-Mobile has over 29,000 of its web pages crawled and indexed by Google. Do you want to know how this is possible?
T-Mobile optimized its website and all web content using the enterprise SEO strategies listed above to improve its visibility in the organic search results.
T-Mobile utilized keyword-optimized templates and data entry that allow for the bulk creation of pages. This practice may not work for small businesses — since they haven’t established a level of trust as large companies such as T-Mobile.
T-Mobile adopted a thoughtful keyword selection, which was integrated into the categorization and navigation structures of its website.
The company ensured an accurate data entry system, which contains content that is unique, valuable, and well-optimized with rich keywords.
It also adopted keyword-rich categories and subcategories. Here’s a great example of one of T-Mobile’s web pages.
Airtel
Despite having a very good presence and authority in the telecom sector, Airtel had poor visibility in the top three search results for postpaid, prepaid and DTH related keywords.
More so, the company faced low rankings for local keywords for Broadband and Postpaid Lines of Business (LOB).
The first SEO strategy adopted was finding striking distance keywords in the top 10 search results. With these keywords, on-page SEO elements and content for all the target landing pages were optimized and improved.
But that’s not all. Aggressive strategic link building was performed to improve the authority and popularity of the company’s website and all web and landing pages were improved and optimized for site speed.
Within a few months of implementing these enterprise SEO strategies, Airtel ranking on Google did not only increase drastically but the company experienced a 3,500% increase in organic traffic.
Conclusion
There you have it, the 5-step process we implement to rank any enterprise website on Google top 10 organic results pages.
Remember to develop an enterprise SEO strategy that will guide every process you take.
The steps above aren’t set on a stone — we may tweak any or all of the steps to suit any large business. It all depends on their goals, and what they intend to achieve with digital marketing.
There is a risk of launching a failed SEO campaign if the SEO strategy is not well-planned, understood, accepted, and supported by all management teams who have a connection to the company.




